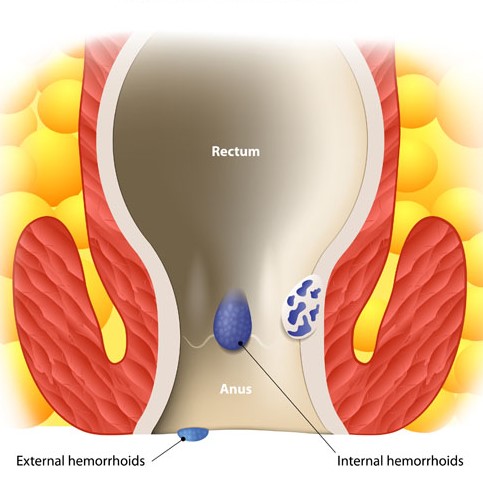
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the lowest part of your rectum and anus. Sometimes the walls of these blood vessels stretch so thin that the veins bulge and get irritated, especially when you defecate. Hemorrhoids are one of the most common causes of rectal bleeding, but are rarely dangerous and usually clear up in a couple of weeks. Internal hemorrhoids are far enough inside the rectum that you can’t usually see or feel them. They are generally a cause of painless bleeding. External hemorrhoids are under the skin around the anus, where there are many more pain-sensing nerves, so they tend to hurt as well as bleed. Constipation and straining during bowel movements can aggravate hemorrhoids. Luckily, the majority of patients with hemorrhoids do not need surgery and improve with medical management using stool softeners and topical creams. However, a minority of patients either do not improve, or have symptoms that are severe enough to warrant surgery before medical management has time to become effective. In these patients hemorrhoids can be removed surgically, either by banding, (which is performed in the office), or hemorrhoidectomy, which is performed in the operating room.