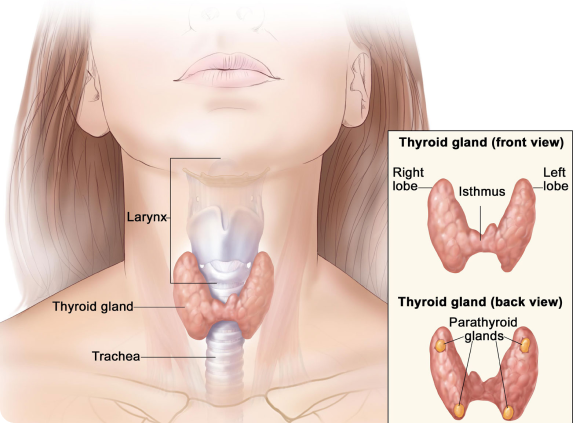
The thyroid gland is located in the neck and it produces thyroid hormone, which helps regulate metabolism. Surgery on the thyroid gland is performed for both malignant and benign disease. The amount removed depends upon the reason the surgery is being performed. A thyroidectomy is typically an inpatient surgery that involves an overnight stay, though many practices perform outpatient surgery as well.
Surgery is typically performed for the following reasons:
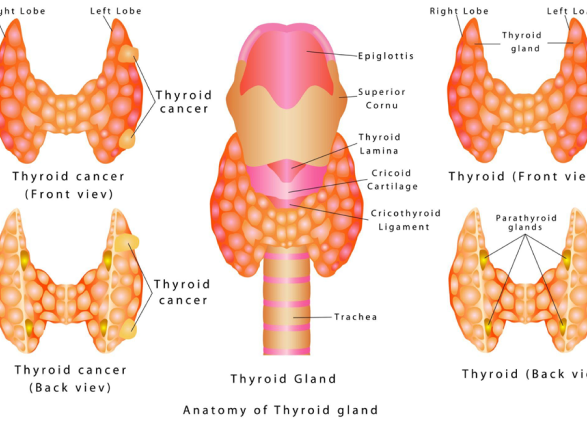
There are several conditions that may require thyroid surgery. However, mainly thyroid surgery is required in the patients who have been diagnosed with thyroid cancer, thyroid nodules that are at least 1cm in size and growing, and patients who have excessive production of thyroid hormones.
Abnormal thyroid hormone levels in the body can cause various signs and symptoms that include:
The removal of thyroid gland is called thyroidectomy. There are 2 kinds of thyroid surgeries:
The surgeon and the physician together will help you decide when to get the thyroid surgery.
Thyroid surgery is an open procedure which is performed via a small collar incision in your neck. The thyroid gland is carefully removed from the surrounding tissue, taking care not to injure the important nerves and vessels in the area, and also taking care not to injure the parathyroid glands, which reside under the thyroid. After performing the surgery, sutures are applied which dissolve overtime. The scar fades away slowly and the time varies from person to person. Most of the patients go home either after surgery or the next day.
You will have to visit your surgeon one week after the surgery. If you have undergone partial thyroidectomy, you will likely not need to take thyroid medication. If you have undergone a total thyroidectomy, you will be put on supplemental thyroid medication because your body loses the ability to produce thyroid hormone.

© 2025, Rath Surgical Group | All rights reserved.